Anyone can post a story online and news travels fast on social media. So we need to question what we read and watch, before trusting that it's right.

Define the task
Understand exactly what the question is asking, so you know how to answer it really well.
Locate information
Find great resources quickly and easily with some simple search techniques.
Select resources
Learn how to choose the best, most reliable information to use in your assignment.
Organise notes
Turn your information into a good set of notes that will make the writing process quicker and easier.
Present the ideas
Plan the points you want to make, and decide how you want to make them.
Find more information at ERGO - State Library of Victoria
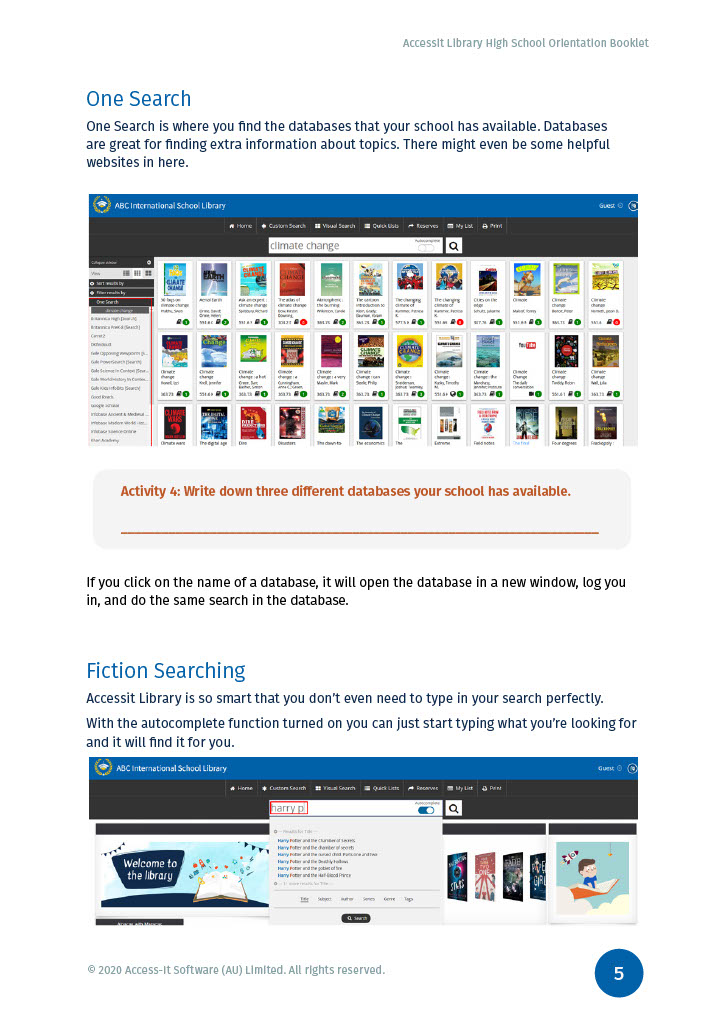
What is a search engine?
Web platform allow you to search the WWW (World Wide Web) Example : Google, Internet Explorer, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo, Bing
What is a database?
A collection of information, often by subject, selected by experts and peer reviewed to ensure the information is accurate, up-to-date and complete
Wikipedia – Online encyclopedia
Wikipedia is a free online encyclopedia, created and edited by volunteers around the world and hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation.
• A primary source provides direct or firsthand evidence about an event, object, person, or work of art. These include historical and legal documents, eyewitness accounts, results of experiments, statistical data, surveys, pieces of creative writing, audio and video recordings, speeches, and art objects.
• In contrast, secondary sources describe, discuss, interpret, comment upon, analyse, evaluate, summarise, and process primary sources. Secondary source materials can be articles in newspapers or popular magazines, book or movie reviews, or articles found in scholarly journals that discuss or evaluate someone else's original research.




Many students use Google as their first source of information. However, you need to be more careful evaluating information found on Google than when using Library resources. Material may be :
You can also end up with so many results that it is difficult to sift through and find the best information
Unlike formally published works, anyone can upload material to the internet, without any quality control processes. In comparison, library materials are selected in conjunction with teaching staff to ensure quality and relevance to your study.
Advanced search Google's advanced search helps you refine and limit your search without having to use the terminology below. All of the refinements below, and more, are available using the advanced search screen.
Domain: Information at the end of the URL relates to the domain of that website e.g
Limit your search to a specific domain by entering it in the search box
For example: domain:edu
Exclude terms - use the minus sign to exclude terms from your search
For example: windows -Microsoft
Expand your search - use OR between search terms to find results containing any of the terms used (otherwise results will only include those that contain all the search terms)
For example: Dogs OR Wolves
Phrase search - use quotation marks to search for exact phrases
For example: "Charles Dickens"
Result types - limit your results to specific types of items by clicking the category you want on the search result screen
For example: images
You can also search for a specific type of file by selecting the format you want (e.g. PDF, html) in the advanced search screen
Truncation - use * to include various endings in your search
For example: nurs* will return results for nurse, nurses, nursing etc.
Understanding your search results
Google returns search results in relevance order, based on a very complicated formula. The highest ranked hits may not be the most suitable ones for you - refining your search can help give better results.
For more information:
Google's online help centre
In some cases, an internet search is a great place to find information. Freely available, quality information sources include:
Google scholar limits results from a standard google search to scholarly and research material. Results come from individual authors, Institutional repositories, academic publishers and more. Resource types include:
Google scholar includes some material that is freely available online, and some that requires a payment to view.
If Google scholar results include books for which only a limited portion of text is accessible, check the library catalogue for a copy that you can borrow instead.
Where search results include more than one version of the same article, the full text may be available on some, but not others.
Scholar also provides details of how many times results have been cited by other articles, and links to related articles.
The general google search tips on this page also apply to Google scholar.
For more information:
Strengths
1. Wikipedia is completely free, providing access to information on millions of topics to anyone with Internet capabilities.
2. Wikipedia is constantly updated by the hour. In comparison, print encylopedias are usually updated annually.
3. Wikipedia is a great place to start your research, giving you background information on your topic and possible keywords to help you conduct more in-depth research elsewhere.
4. Sources used in the articles are cited, allowing further investigation into any topic.
1. Anyone can create, edit, or delete Wikipedia articles.
2. Wikipedia articles cannot be considered scholarly, because we know nothing about the contributors.
3. Articles are works-in-progress, meaning changes are constantly occuring to the information. When an article is first published, the information might waver back and forth between viewpoints before achieving a neutral tone. Viewing the behind-the-scenes discussion can be a valuable way of learning about those varying perspectives.
4. Sometimes articles are vandalized, whether for fun, as a hoax, or because the subject is controversial.
5. The intended audience can vary-- some articles are written from a insider's view, with highly technical language, while some are written for a more general audience. This can be both frustrating and valuable depending on what one is looking for, and either way is a warning sign that the information can be inconsistent.
Text from University of Pittsburgh
Website domains can give you information about who the author is, and the reliability of the content:
| .com | commercial, business - needs to be carefully evaluated |
|
.edu |
educational - usually a good source of information |
|
.gov |
government - usually a good source of information |
|
.org |
organisational, non-profit - needs to be carefully evaluated |
|
.au .uk .ca |
The two letter abbreviation tells you the country the website is from (e.g. Australia, UK, Canada) |
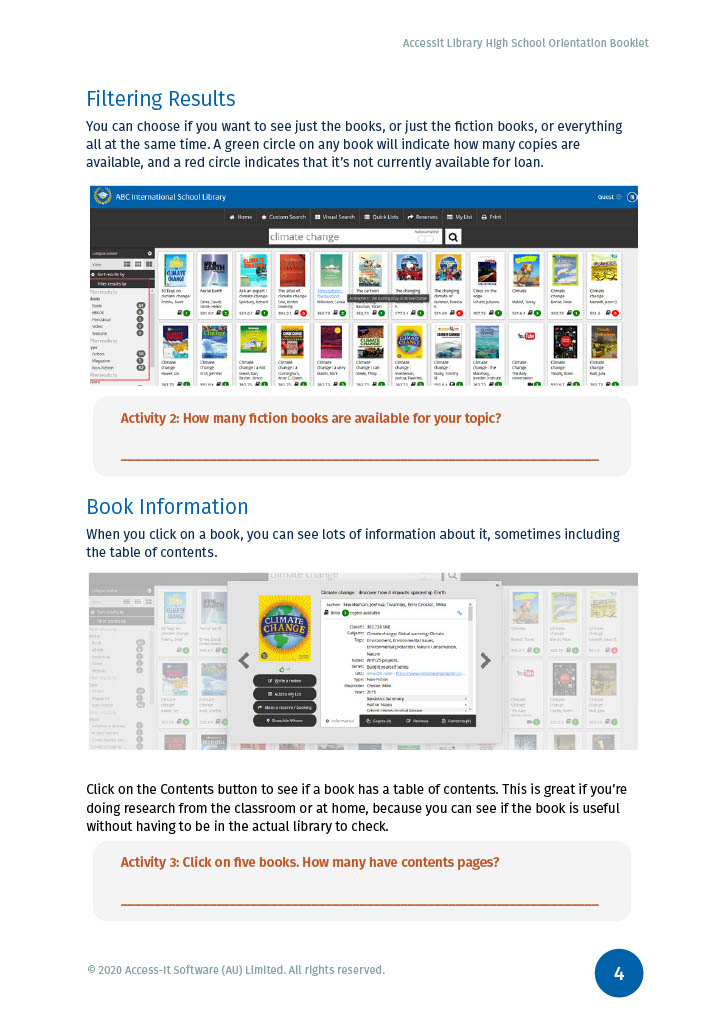
Evaluating the information sources that you use is important to give credibility to your work. This is particularly important with material that is found on the World Wide Web but it also applies to information found in books, journals, magazines and reports.There are vast amounts of information available, but it is essential to identify resources that are suitable, reliable and factual for your assignments.
These guidelines will help you assess the quality and suitability of information you find. Ask yourself -
Who wrote it?
Who is the creator of the website or author of the content? Can they be easily identified?
Can you find information about the author’s qualifications or background? Are any qualifications relevant to the topic they are writing on?
Does author have any affiliations with any Institutions or organisations? Is the organisation reputable? Are they neutral, or do they have a vested interest in the topic?
Is the work self-published or is a reputable publisher involved?
What?
When?
Finding satisfactory answers to these questions is an indication that you can rely on the information you have gathered. It is better to use a few good quality resources than to include a lot of poor quality ones.
Not all note taking styles work for everyone. Your preferred note taking style will depend on what your learning style is (Visual, Auditory, Kinasthetic or Read & Write). E.g. Visual learners might benefit from using diagrams, pictures, or coloured highlighters.
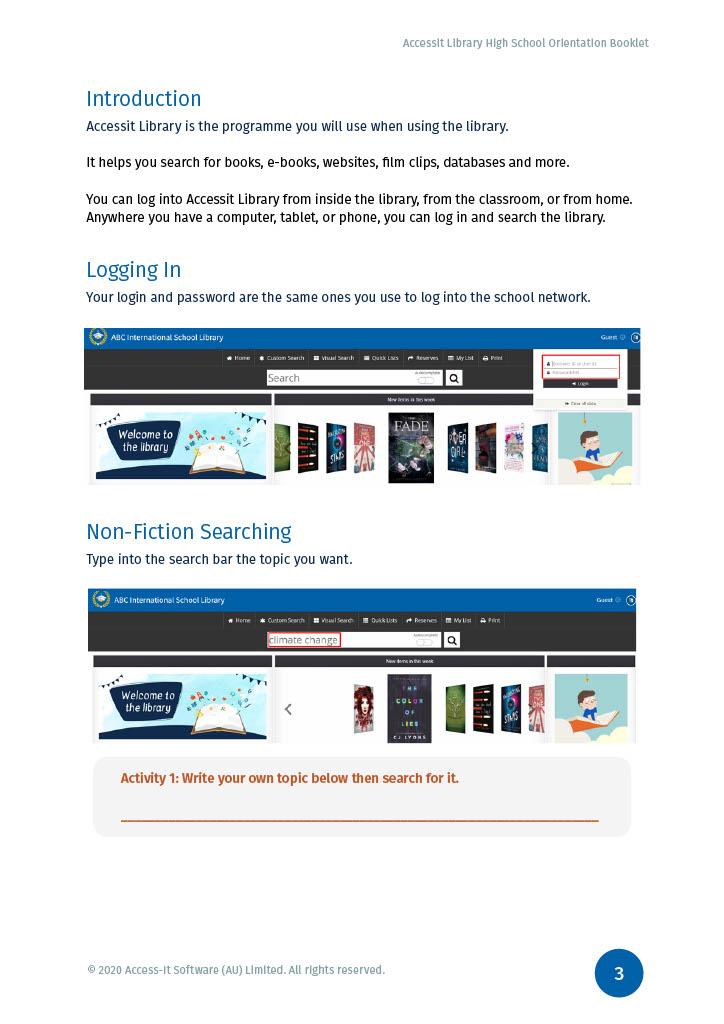
Explore the different note taking techniques.
Referencing (also known as citing or acknowledging your source) means showing in your assignment the sources you have used to develop your ideas. A reference includes:
A mention of the source in the text of your assignment (this might be a general reference to the author, a quotation, or paraphrasing/summarising ideas from the original source).
Full details of the source (e.g. author, year, title, source and volume/page details, URL) in a reference list at the end of your assignment - usually ordered alphabetically by author's surname.
Two referencing systems are used at Northcote High School - APA and Harvard referencing. Check with your teacher to see which one you should use. The latest style of APA is the 7th edition, but check with your teacher which edition they would like you to use.
Both are "Author-date" systems which means the citation within the text looks like this:
Referencing systems have rules about how to format your references, for example:
In the bibliography, a reference using Harvard would look like this:
Using APA, the reference would look slightly different:
If a piece of information is common knowledge (known by a lot of people or available from a large number of sources), there is no need to provide a reference. For example - Canberra is the capital of Australia; the 1956 Summer Olympics were held in Melbourne.
A reference list, generally, contains only sources you have cited in-text in your assignment.
A bibliography, generally, is a list of all the sources you used to generate your ideas about the topic including those cited in your assignment as well as those you did not cite.
However, the terms reference list and bibliography are sometimes used interchangeably so it is very important to check with your teacher to make sure you know what is required for your assignment
Reference generators are a quick way to reference your work but they are not always accurate. If using a reference generator make sure to check for errors before submitting your assignment.
Plagiarism is using someone else's words and presenting them as your own. Sometimes plagiarism is deliberate, but it can also happen unintentionally. Some examples of plagiarism are:
Consequences for plagiarism can be serious, particularly if you go on to study at university.
Anyone can post a story online and news travels fast on social media. So we need to question what we read and watch, before trusting that it's right.